random_signal_generator is a c++ package that generates smooth, random data signals.
This pacakge includes:
- A library for integrating with your own code
- An executable for generating signals directly from the command line
Randomly generated signals are useful data sets for testing and tuning algorithms. Common applications include:
- Machine Learning
- Signal Processing
- Control Theory
- Forecasting
License: MIT
Table of Contents:
- Download: Where to download the source code from.
- Installation: How to install the utility on your system.
- Usage: How to use this package's library in your code or executable on the command line.
- How It Works: Explains how the random signals are generated.
1: Download
Stable Release: https://github.com/pcdangio/random_signal_generator/releases/latest
Latest Source: https://github.com/pcdangio/random_signal_generator/archive/master.zip
GitHub Repository: https://github.com/pcdangio/random_signal_generator
2: Installation
First, download the latest source code from GitHub.
Next, run the following commands in the repo's directory to build the package from source and install it to your system:
This will build and install the library and executable to the default CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX path, which is:
- Linux:
/usr/local - Windows:
C:/Program Files/random_signal_generator
You may change the install path by passing -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX "some_path" when calling cmake.
3: Usage
This section will explain how to use the library and executable included in this package. Full documentation of the code, including the library interface, can be found here: https://pcdangio.github.io/doc/utilities/random_signal_generator/index.html
3.1: Using the Library:
The following example displays how to use the library in your own code. Full documentation of the library can be found here
Code
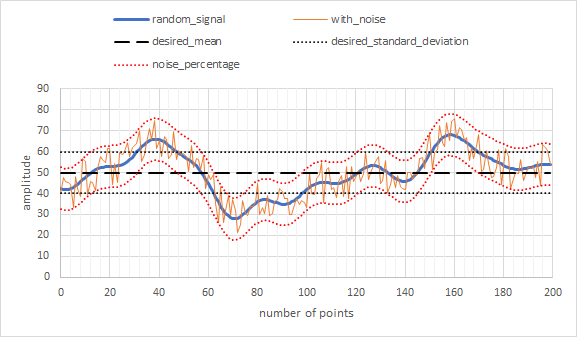
Figure 2 below shows how each of the parameters affects the shape of the generated signal. In this scenario, n_points = 200, desired_mean = 50, desired_standard_deviation = 10, and noise_percentage = 1.0 (100% of desired_standard_deviation).
Compiling
The following example shows how to build your project on Linux and link it against the pcd-random_signal_generator static library:
NOTE This example assumes that you have installed the library and it's headers to a location on your library PATH.
3.2: Command Line Executable
This package installs an executable named random_signal_generator on your system. By default, it should be installed within your PATH, so you should be able to call it directly after installation.
The following code snippet illustrates how the executable should be used:
The following code snippet illustrates two example use cases:
4: How It Works
This utility leverages Fourier Composition to generate random signals.
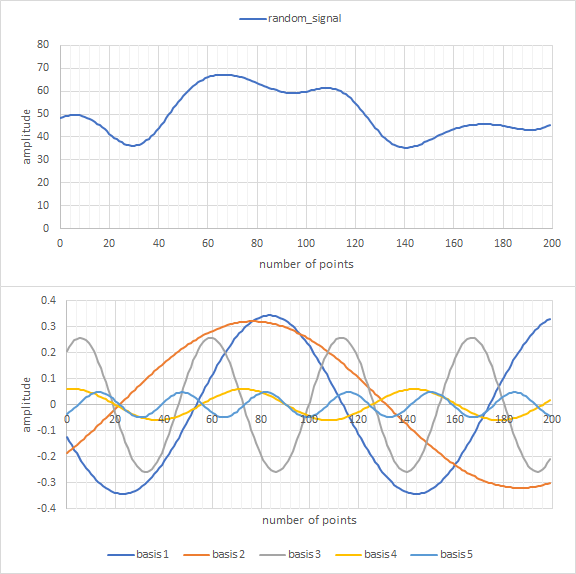
Fourier Series analysis can be used to decompose any periodic signal into an infinite number of sine waves. It then stands that you can use a series of sine waves to compose a new signal. The random_signal_generator library uses this concept to generate pseudo-random signals. The algorithm generates a series of random sine waves, which are then combined into a new signal.
Random sine waves are calculated by choosing a random amplitude, frequency, and phase offset for each wave. It is important to note that this algorithm differs from standard Fourier Composition in that the sine waves are NOT harmonic. This limitation allows for non-periodic random signals to be generated. Another feature of this algorithm is that lower frequency waves tend to have higher amplitude, which gives more base structure to the generated signal (e.g. rising, falling, etc.).
Once the random sine waves are generated, they are superimposed (added) together to create the random signal that is output by the utility. An example is provided in Figure 3 below:
 1.8.13
1.8.13